Virtual List
In the Taro application, normal list rendering follows the following logic.
- Generate or load data from a remote
- add the data to the framework's responsive data
- the framework tries to update the view in full depending on the data using the diff algorithm or other mechanism
- the Taro runtime captures the framework's update request to update the view
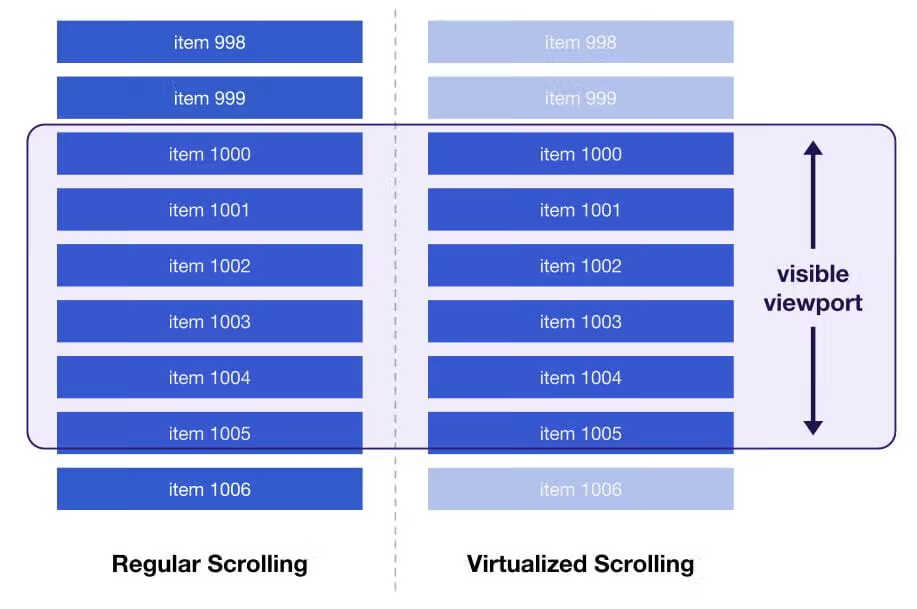
If we follow this logic, we may have serious performance issues when the amount of data we generate or load in the first step is very large, causing the view to be unresponsive to operations for some time. To solve this problem, we can use another approach: instead of rendering the view generated with the full amount of data, we can render only the view in the current visible viewport, and render the view in the non-visible area after the user scrolls to the visible area.
React/Nerv
With React/Nerv we can introduce the VirtualList component directly from @tarojs/components/virtual-list.
import VirtualList from '@tarojs/components/virtual-list'
The simplest long list component would look like this, with all 5 properties of VirtualList as required fields.
function buildData (offset = 0) {
return Array(100).fill(0).map((_, i) => i + offset);
}
const Row = React.memo(({ id, index, style, data }) => {
return (
<View id={id} className={index % 2 ? 'ListItemOdd' : 'ListItemEven'} style={style}>
Row {index} : {data[index]}
</View>
);
})
export default class Index extends Component {
state = {
data: buildData(0),
}
render() {
const { data } = this.state
const dataLen = data.length
return (
<VirtualList
height={500} /* list height */
width='100%' /* list width */
itemData={data} /* rendering data for the list */
itemCount={dataLen} /* length of rendering list */
itemSize={100} /* height of list item */
>
{Row} /* List single component, where only one component can be passed in */
</VirtualList>
);
}
}
Infinite Scroll
Implementing infinite scrolling is also very simple, we just need to append data to the end of the list when it scrolls to the bottom.
const Row = React.memo(({ id, index, style, data }) => {
return (
<View id={id} className={index % 2 ? 'ListItemOdd' : 'ListItemEven'} style={style}>
Row {index} : {data[index]}
</View>
);
})
function buildData (offset = 0) {
return Array(100).fill(0).map((_, i) => i + offset);
}
export default class Index extends Component {
state = {
data: buildData(0),
}
loading = false
listReachBottom() {
Taro.showLoading()
// If loading is related to the view, then it should be in `this.state`
// We are using a synchronous API to call loading here, so we don't need
this.loading = true
setTimeout(() => {
const { data } = this.state
this.setState({
data: data.concat(buildData(data.length))
}, () => {
this.loading = false;
Taro.hideLoading()
})
}, 1000)
}
render() {
const { data } = this.state
const dataLen = data.length
const itemSize = 100
return (
<VirtualList
className='List'
height={500}
itemData={data}
itemCount={dataLen}
itemSize={itemSize}
width='100%'
onScroll={({ scrollDirection, scrollOffset }) => {
if (
// 避免重复加载数据
!this.loading &&
// 只有往前滚动我们才触发
scrollDirection === 'forward' &&
// 5 = (列表高度 / 单项列表高度)
// 100 = 滚动提前加载量,可根据样式情况调整
scrollOffset > ((dataLen - 5) * itemSize + 100)
) {
this.listReachBottom()
}
}}
>
{Row}
</VirtualList>
);
}
}
props
children: ReactComponent
The single component of the list to be rendered. The component's props has 4 properties.
style: the style of the single item, the style must be passed into the component'sstyledata: the data rendered by the component, same as the virtual listitemDataindex: the index of the data rendered by the componentisScrolling: whether the component is scrolling, returns a boolean value whenuseIsScrollingistrue, otherwise returnsundefined
PureComponentor useshouldComponentUpdate()` to optimize this component and avoid unnecessary rendering.
itemCount: number
The length of the list. Required field.
itemData: Array<any>
Render data. Required field.
itemSize: number
The size of the list item, height when scrolling vertically, width when scrolling horizontally. Required field.
height: number | string
The height of the list. Required when the scroll direction is vertical.
width: number | string
The width of the list. Required when the scroll direction is horizontal.
className: string
Root Component CSS Class
style: Style
Style of the root component
initialScrollOffset: number = 0
The initial scroll offset value, horizontal scrolling affects scrollLeft, vertical scrolling affects scrollTop.
innerElementType: ReactElement = View
List internal container component type, default value is View. The parentNode of this container is ScrollView and childNodes is the list.
innerRef: Ref | Function
The ref of the inner container component of the list.
layout: string = 'vertical'
Scrolling direction. vertical is vertical scrolling, horizontal is parallel scrolling. Default is vertical.
onScroll: Function
The function is called when the list is scrolled. The first argument of the function is an object, consisting of three properties.
scrollDirection, the scroll direction, possible values areforwardforward,backwardbackward.scrollOffset, the scroll distancescrollUpdateWasRequested, returnstruewhen scrolling is called byscrollTo()orscrollToItem(), otherwise returnsfalse
onScrollNative: Function
Call the platform's native scroll listener function.
overscanCount: number = 1
The higher the value of the number of list items rendered outside the visible area, the lower the probability of a white screen when scrolling fast, and accordingly, the worse the performance per scroll will become.
unlimitedSize?: boolean
To unlock the height list single item size limit, use the default value: itemSize (please note that too large a difference between the initial height and the actual height can cause hidden problems).
position?: 'absolute' | 'relative'
Layout method, the default is "absolute"
renderBottom?: ReactNode
Bottom area
useIsScrolling: boolean
Whether to inject the isScrolling property into the children component. This parameter is generally useful when implementing a scrolling skeleton screen (or other placeholder).
Other parameters of the ScrollView component
In addition to the above parameters, all parameters of the ScrollView component can be passed to the VirtualList component, and the parameters described in the above document are preferred in case of conflicts.
Methods
The ref is created with React.createRef() and mounted on VirtualList to access the internal methods of VirtualList.
export default class Index extends Component {
state = {
data: buildData(0),
}
list = React.createRef()
componentDidMount() {
const list = this.list.current
list.scrollTo()
list.scrollToItem()
}
render() {
const { data } = this.state
const dataLen = data.length
return (
<VirtualList
height={500} /* list height */
width='100%' /* list width */
itemData={data} /* rendering data for the list */
itemCount={dataLen} /* length of rendering list */
itemSize={100} /* height of list item */
ref={this.list}
>
{Row}
</VirtualList>
);
}
}
scrollTo(scrollOffset: number): void
Scroll to the specified location.
scrollToItem(index: number, align: string = "auto"): void
Scrolls to the specified entry.
The second parameter align may have the following values.
auto: the minimum possible scrolling distance to ensure that the entry is in the visible area, or not scrolling if it is already in the visible areasmart: if the item is already in the visible area, don't scroll; if it is partially in the visible area, scroll as far as possible to keep the item in the visible area; if the item is not in the visible area at all, then scroll until the item is centered in the visible areacenter: center the item in the visible areaend: make the entry appear at the end of the viewable areastart: puts the item at the end of the viewable area
Vue
To use virtual lists in Vue, we need to declare in the entry file the use of.
// app.js entry file
import Vue from 'vue'
import VirtualList from '@tarojs/components/virtual-list'
Vue.use(VirtualList)
The simplest long list component would look like this, with all 5 properties of virtual-list as required fields.
<! –– row.vue Single-item components ––>
<template>
<view
:class="index % 2 ? 'ListItemOdd' : 'ListItemEven'"
:style="css"
>
Row {{ index }} : {{ data[index] }}
</view>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['index', 'data', 'css']
}
</script>
<! –– page.vue page component ––>
<template>
<virtual-list
wclass="List"
:height="500"
:item-data="list"
:item-count="list.length"
:item-size="100"
:item="Row"
width="100%"
/>
</template>
<script>
import Row from './row.vue'
function buildData (offset = 0) {
return Array(100).fill(0).map((_, i) => i + offset)
}
export default {
data() {
return {
Row,
list: buildData(0)
}
},
}
</script>
infinite scrolling
Implementing infinite scrolling is also very simple, we just need to append data to the end of the list when it scrolls to the bottom.
<template>
<virtual-list
wclass="List"
:height="500"
:item-data="list"
:item-count="dataLen"
:item-size="itemHeight"
:item="Row"
width="100%"
@scroll="onScroll"
/>
</template>
<script>
import Row from './row.vue'
function buildData (offset = 0) {
return Array(100).fill(0).map((_, i) => i + offset)
}
export default {
data() {
return {
Row,
list: buildData(0),
loading: false,
itemHeight: 100
}
},
computed: {
dataLen () {
return this.list.length
}
},
methods: {
listReachBottom() {
Taro.showLoading()
this.loading = true
setTimeout(() => {
const { data } = this.state
this.setState({
data: data.concat(buildData(data.length))
}, () => {
this.loading = false;
Taro.hideLoading()
})
}, 1000)
},
onScroll({ scrollDirection, scrollOffset }) {
if (
// Avoid duplicate data loading
!this.loading &&
// Only scrolling forward we trigger
scrollDirection === 'forward' &&
// 5 = (List height / Single item list height)
// 100 = Rolling advance loading amount, adjustable according to the style
scrollOffset > ((this.dataLen - 5) * this.itemHeight + 100)
) {
this.listReachBottom()
}
}
}
}
</script>
props
item: VueComponent
The single component of the list to be rendered. The component's props has 4 properties.
css: the style of the single item, the style must be passed into the component'sstyledata: the data rendered by the component, same as the virtual listitemDataindex: the index of the data rendered by the componentisScrolling: whether the component is scrolling or not, returns a boolean value whenuseIsScrollingistrue, otherwise returnsundefined
itemCount: number
The length of the list. Required field.
itemData: Array<any>
Render data. Required field.
itemSize: number
The size of the list item, height when scrolling vertically, width when scrolling horizontally. Required field.
height: number | string
The height of the list. Required when the scroll direction is vertical.
width: number | string
The width of the list. Required when the scroll direction is horizontal.
wclass: string
Root Component CSS Classes
wstyle: Style
Style of the root component
initialScrollOffset: number = 0
The initial scroll offset value, horizontal scrolling affects scrollLeft, vertical scrolling affects scrollTop.
innerElementType: string = 'view'
List internal container component type, default value is view. The parentNode of this container is scroll-view and childNodes is the list.
layout: string = 'vertical'
Scrolling direction. vertical is vertical scrolling, horizontal is parallel scrolling. Default is vertical.
v-on:scroll: Function
The function is called when the list is scrolled. The first argument of the function is an object, consisting of three properties.
scrollDirection, the scroll direction, possible values areforwardforward,backwardbackward.scrollOffset, the scroll distancescrollUpdateWasRequested, returnstruewhen scrolling is called byscrollTo()orscrollToItem(), otherwise returnsfalse
scrollNative: Function
Call the platform's native scroll listener function. Note that the call to pass this function uses v-bind instead of v-on.
<virtual-list
wclass="List"
:height="500"
:item-data="list"
:item-count="list.length"
:item-size="100"
:item="Row"
width="100%"
@scroll="onScroll"
:scroll-native="onScrollNative"
/>
overscanCount: number = 1
The higher the value of the number of list items rendered outside the visible area, the lower the probability of a white screen when scrolling fast, and accordingly, the worse the performance per scroll will become.
useIsScrolling: boolean
Whether to inject the isScrolling property into the item component. This parameter is generally useful when implementing a scrolling skeleton screen (or other placeholder).
Related Questions
- Baidu smart program temporarily does not support the use of virtual list components, see #7254
- The virtual list component needs to implement a version of
Vue3(to be implemented), see [Vue3 Other Restrictions](https://taro-docs.jd.com/taro/docs/vue3#Other Limitations)